Understanding direct cooling vs indirect cooling helps you choose the right refrigeration structure for your supermarket. Direct cooling cools products inside each cabinet, while an indirect cooling system distributes cold through a secondary medium, offering better stability for large-scale retail environments. This article will explain in detail the differences between direct cooling and indirect cooling.
Before selecting equipment, you should understand how each system performs in real supermarket conditions.
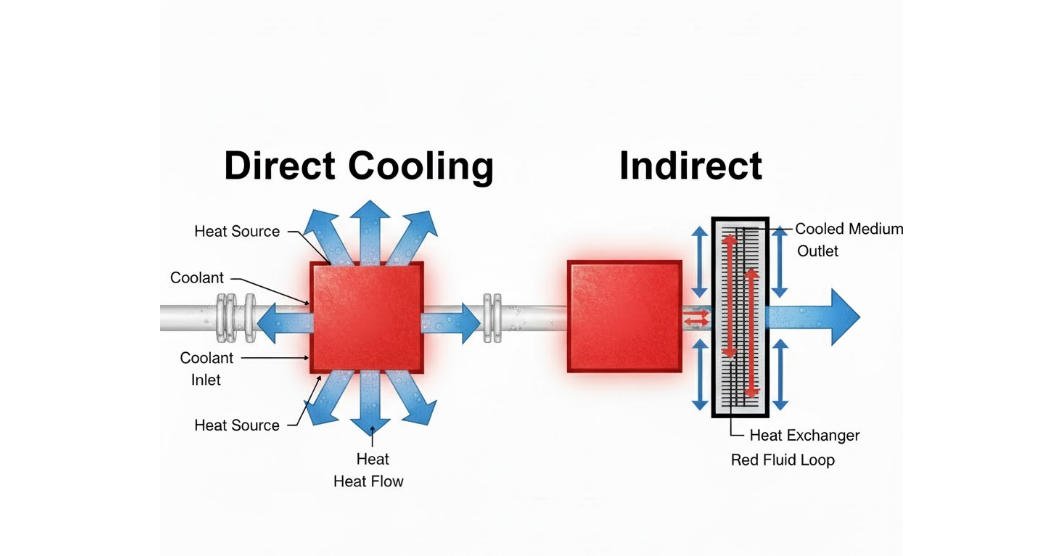
What Is Direct Cooling?
When you ask what is direct cooling, you are referring to a refrigeration method where the refrigerant circulates directly through the evaporator installed inside the cabinet. Heat is absorbed straight from the stored products and internal air, resulting in a fast cooling response and efficient temperature pull-down.
Because each unit operates independently, direct cooling is especially suitable for flexible store layouts and frequent equipment adjustments. It is widely applied in Display Refrigerators, Air Curtain Refrigerators, and Salad Bar Refrigerators used in high-traffic retail areas where quick recovery and cost control are essential.
What Is an Indirect Cooling System?
An indirect cooling system uses refrigerant only to cool a secondary medium, such as chilled air or a cooling liquid, which then transfers cold energy to the display cabinet. By separating the refrigerant circuit from the sales area, this system provides more uniform temperature distribution and reduces frost formation and moisture loss on food surfaces.
This design is particularly valuable for fresh food zones where stable temperature and humidity directly affect product quality and shelf life. Indirect cooling is commonly chosen for long display lines and premium supermarket environments, supporting consistent food presentation.
Examples of Indirect Cooling Systems in Supermarkets
In modern supermarkets, indirect cooling systems are commonly applied in areas that require consistent temperature control across long display lines. Typical examples include supermarket meat display cases, air-cooled display cases, and beverage cabinets. These systems use centrally distributed chilled air to ensure uniform cooling across multiple cabinets.
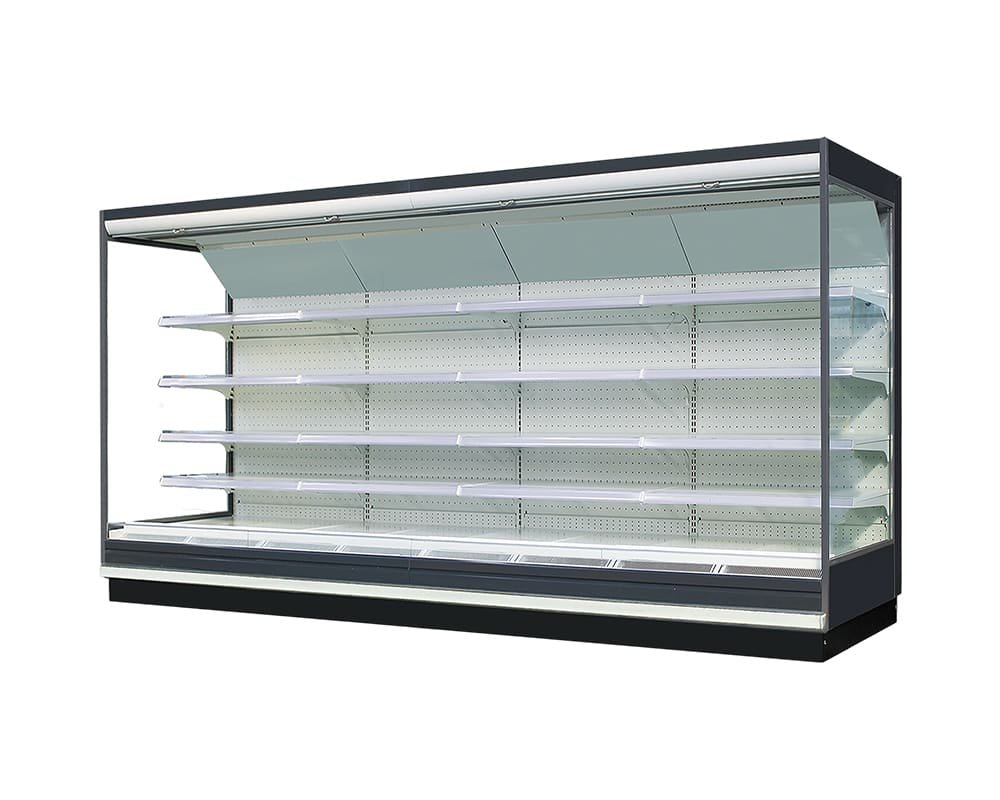

By supporting long-distance and modular displays, indirect cooling systems minimize temperature variation between cabinets, reduce product dehydration, and maintain a clean, open store appearance.
Direct Cooling vs Indirect Cooling: Key Technical Differences
When you evaluate direct cooling and indirect cooling, you are not simply comparing technologies. You are choosing how your refrigeration system will support store layout, expansion plans, and daily operational efficiency.
System structure
With direct cooling, each cabinet functions as an independent unit. This gives you greater freedom in placement, easier equipment replacement, and more flexibility when adjusting store layouts. Indirect cooling systems operate through centralized distribution, allowing multiple cabinets to share one cooling source and operate under unified control.
Temperature performance
Direct cooling meets the requirements of standard retail refrigeration and performs well in most general applications. Indirect cooling systems, however, provide superior temperature uniformity, which is essential for fresh food, meat, and premium displays.
Investment and scalability
Direct cooling solutions involve lower initial investment and are well suited to step-by-step store upgrades or smaller retail formats. Indirect cooling systems require higher upfront cost and professional planning, but they offer long-term advantages in large supermarkets with extensive display lines.
Merchandising impact
Direct cooling supports practical and efficient product presentation. Indirect cooling enhances freshness, visual continuity, and overall store appearance, helping create a more refined shopping environment that encourages customer engagement.
This comparison highlights how each cooling approach aligns differently with supermarket size, merchandising goals, and operational strategy.
Summarize: Direct Cooling vs Indirect Cooling
| Decision Factor | Direct Cooling | Indirect Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling method | Cabinet-based | Centralized distribution |
| Temperature consistency | Standard | High |
| Initial investment | Lower | Higher |
| Best application | Small to mid-size stores | Large supermarkets |
| Food presentation | Functional | Premium |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Direct Cooling and Indirect Cooling
Understanding the specific strengths and limitations of each cooling system allows you to select the most suitable solution for your store size, product range, and operational goals.
Advantages Comparison
| Feature | Direct Cooling | Indirect Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Installation & Deployment | Quick setup, independent cabinets, flexible layout | Supports large-scale centralized systems, consistent cooling across multiple units |
| Upfront Cost | Lower, cost-effective for small to mid-size stores | Justified by long-term stability and reduced product loss |
| Maintenance | Simple troubleshooting, easy cabinet replacement | Centralized control simplifies monitoring and reduces manual intervention |
| Temperature & Humidity Control | Reliable for standard products | High, stable temperature and humidity for premium fresh foods |
| Merchandising Impact | Functional, practical display | Premium visual continuity, ideal for long display lines |
Disadvantages Comparison
| Feature | Direct Cooling | Indirect Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature & Humidity Control | Can vary between cabinets, less precise | Requires professional system design and installation |
| Food Preservation | Limited control may affect fresh product shelf life | Higher initial investment and maintenance complexity |
| System Complexity | Simple but less scalable for large layouts | Complex setup, requires trained technicians |
| Investment & Planning | Cost-effective but may not suit large supermarkets | Higher upfront cost may deter small-scale applications |
Add Your Direct Cooling Island Freezer and Supermarket Style Freezer in Eddysen
By choosing Eddysen, you partner with experienced Supermarket Refrigerator Manufacturers and reliable Supermarket Display Refrigerator Suppliers. Our direct cooling island freezers and supermarket style freezers are designed to integrate seamlessly into your store layout, ensuring optimal product display and long-term operational efficiency.
With nearly 20 years of experience in commercial refrigeration and kitchen equipment manufacturing, Eddysen combines advanced industrial design and strict quality control to deliver durable, energy-efficient, and cost-effective cold chain solutions. Our expertise allows us to provide customized solutions that meet the specific needs of supermarkets, convenience stores, fresh food markets, and large-scale retail environments, helping you enhance product freshness and improve customer satisfaction. Contact us now to get a quote for supermarket refrigeration equipment.
In Conclusion
Direct cooling prioritizes flexibility and cost efficiency, while indirect cooling delivers stability and premium presentation.
Your ideal choice depends on your store size, product mix, operational priorities, and long-term goals. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each system, you can select a refrigeration solution that maximizes product freshness and reduces energy consumption.


